13
Dec
Horn of Africa’s Growth Challenges Amid Youthful Population and Renewable Energy Dependence
The Horn of Africa, home to a predominantly young population (70% under 25) and heavily reliant on renewable energy (85%), holds considerable growth potential. A new UNDP report highlights critical issues in the region. Challenges such as low intra-regional trade, rising climate change impacts, and political instability hinder progress. To unlock sustainable economic growth, addressing these barriers is essential.
RELATED
Posts
4
Mar
Revisiting the Scheme to Recast the Red Sea as an Arab Lake
The "Red Sea Arab Lake" Doctrine, also described as the...
4
Mar
Sudan's Allegation & Ethiopia’s Strategic Crossroads
The relationship between Addis Ababa and Khartoum, already tense due...
4
Mar
GERD Negotiations and Egypt’s Strategic Objectives: Baselines, Control, and the Securitization of the Nile
Since the launch of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD),...
4
Mar
Shaping the Horn: Turkey’s Strategic Role in Somalia and the Red Sea Basin
Since establishing the TURKSOM military training mission in Somalia...
4
Mar
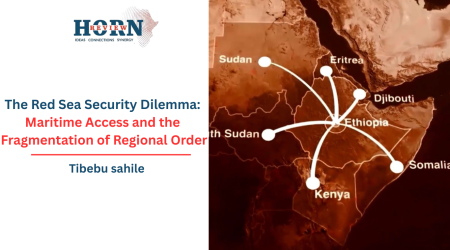
The Red Sea Security Dilemma: Maritime Access and the Fragmentation of Regional Order
In recent years, the Red Sea has shifted from a...
4
Mar
The Fallacy of Power: Sudan’s Warring Factions and the AU’s Path to Legitimate Governance
Sudan’s ongoing war is not a confrontation between a legitimate...
4
Mar
Beyond Basin Diplomacy: The Cairo Meeting and Egypt’s Strategy in South Sudan
The February 2026 Cairo meeting between Egyptian Foreign Minister...
4
Mar
Egypt’s Strained Financing for Kenya’s Dam
Egypt's move into Kenyan water projects with that $100...
4
Mar
The Quad & Sudan's Mediator Paradox
Sudan's unraveling reveals a deeper truth than any body count...